
- Current
- Browse
- Collections
-
For contributors
- For Authors
- Instructions to authors
- Article processing charge
- e-submission
- For Reviewers
- Instructions for reviewers
- How to become a reviewer
- Best reviewers
- For Readers
- Readership
- Subscription
- Permission guidelines
- About
- Editorial policy
Search
- Page Path
- HOME > Search
- Drug Regimen
- The Efficacy and Safety of Moderate-Intensity Rosuvastatin with Ezetimibe versus High-Intensity Rosuvastatin in High Atherosclerotic Cardiovascular Disease Risk Patients with Type 2 Diabetes Mellitus: A Randomized, Multicenter, Open, Parallel, Phase 4 Study
- Jun Sung Moon, Il Rae Park, Sang Soo Kim, Hye Soon Kim, Nam Hoon Kim, Sin Gon Kim, Seung Hyun Ko, Ji Hyun Lee, Inkyu Lee, Bo Kyeong Lee, Kyu Chang Won
- Diabetes Metab J. 2023;47(6):818-825. Published online November 24, 2023
- DOI: https://doi.org/10.4093/dmj.2023.0171
- 2,415 View
- 245 Download
-
 Abstract
Abstract
 PDF
PDF Supplementary Material
Supplementary Material PubReader
PubReader  ePub
ePub - Background
To investigate the efficacy and safety of moderate-intensity rosuvastatin/ezetimibe combination compared to highintensity rosuvastatin in high atherosclerotic cardiovascular disease (ASCVD) risk patients with type 2 diabetes mellitus (T2DM).
Methods
This study was a randomized, multicenter, open, parallel phase 4 study, and enrolled T2DM subjects with an estimated 10-year ASCVD risk ≥7.5%. The primary endpoint was the low-density lipoprotein cholesterol (LDL-C) change rate after 24-week rosuvastatin 10 mg/ezetimibe 10 mg treatment was non-inferior to that of rosuvastatin 20 mg. The achievement proportion of 10-year ASCVD risk <7.5% or comprehensive lipid target (LDL-C <70 mg/dL, non-high-density lipoprotein cholesterol <100 mg/dL, and apolipoprotein B <80 mg/dL) without discontinuation, and several metabolic parameters were explored as secondary endpoints.
Results
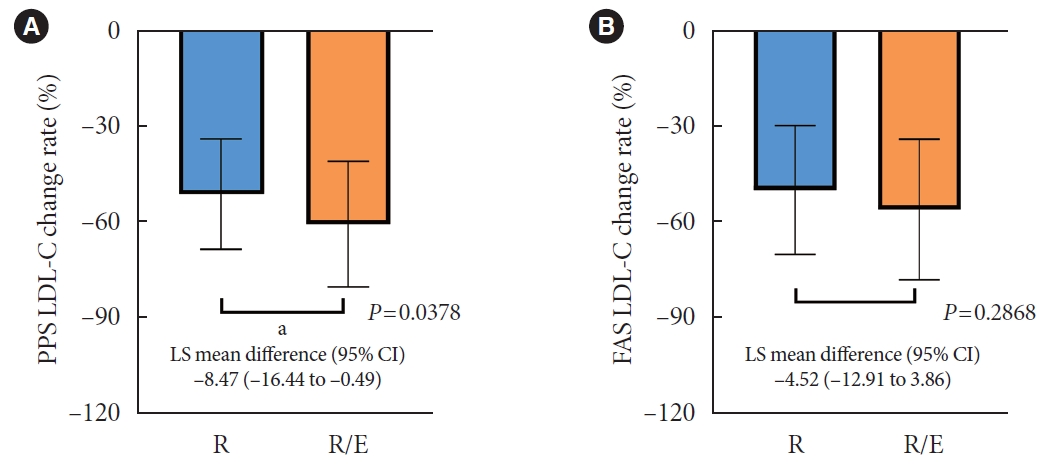
A hundred and six participants were assigned to each group. Both groups showed significant reduction in % change of LDL-C from baseline at week 24 (–63.90±6.89 vs. –55.44±6.85, combination vs. monotherapy, p=0.0378; respectively), but the combination treatment was superior to high-intensity monotherapy in LDL-C change (%) from baseline (least square [LS] mean difference, –8.47; 95% confidence interval, –16.44 to –0.49; p=0.0378). The combination treatment showed a higher proportion of achieved comprehensive lipid targets rather than monotherapy (85.36% vs. 62.22% in monotherapy, p=0.015). The ezetimibe combination significantly improved homeostasis model assessment of β-cell function even without A1c changes (LS mean difference, 17.13; p=0.0185).
Conclusion
In high ASCVD risk patients with T2DM, the combination of moderate-intensity rosuvastatin and ezetimibe was not only non-inferior but also superior to improving dyslipidemia with additional benefits compared to high-intensity rosuvastatin monotherapy.
- Guideline/Fact Sheet
- Sodium-Glucose Cotransporter-2 Inhibitor for Renal Function Preservation in Patients with Type 2 Diabetes Mellitus: A Korean Diabetes Association and Korean Society of Nephrology Consensus Statement
- Tae Jung Oh, Ju-Young Moon, Kyu Yeon Hur, Seung Hyun Ko, Hyun Jung Kim, Taehee Kim, Dong Won Lee, Min Kyong Moon, The Committee of Clinical Practice Guideline, Korean Diabetes Association and Committee of the Cooperative Studies, Korean Society of Nephrology
- Diabetes Metab J. 2020;44(4):489-497. Published online August 21, 2020
- DOI: https://doi.org/10.4093/dmj.2020.0172
- 7,824 View
- 167 Download
- 2 Web of Science
- 3 Crossref
-
 Abstract
Abstract
 PDF
PDF Supplementary Material
Supplementary Material PubReader
PubReader  ePub
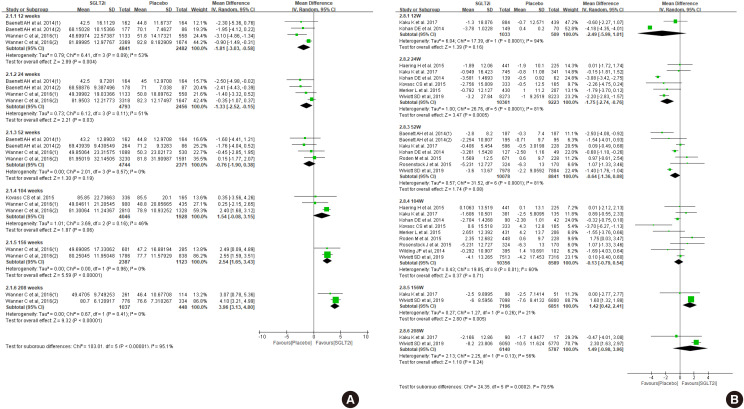
ePub Diabetes is a leading cause of end-stage renal disease. Therefore, prevention of renal dysfunction is an important treatment goal in the management of diabetes. The data of landmark cardiovascular outcome trials of sodium-glucose cotransporter-2 (SGLT2) inhibitor showed profound reno-protective effects. The Korean Diabetes Association and the Korean Society of Nephrology reviewed clinical trials and performed meta-analysis to assess the effects of SGLT2 inhibitors on the preservation of estimated glomerular filtration rate (eGFR). We limited the data of SGLT2 inhibitors which can be prescribed in Korea. Both eGFR value and its change from the baseline were significantly more preserved in the SGLT2 inhibitor treatment group compared to the control group after 156 weeks. However, some known adverse events were increased in SGLT2 inhibitor treatment, such as genital infection, diabetic ketoacidosis, and volume depletion. We recommend the long-term use SGLT2 inhibitor in patients with type 2 diabetes mellitus (T2DM) for attenuation of renal function decline. However, we cannot generalize our recommendation due to lack of long-term clinical trials testing reno-protective effects of every SGLT2 inhibitor in a broad range of patients with T2DM. This recommendation can be revised and updated after publication of several large-scale renal outcome trials.
-
Citations
Citations to this article as recorded by- Real-World Treatment Patterns according to Clinical Practice Guidelines in Patients with Type 2 Diabetes Mellitus and Established Cardiovascular Disease in Korea: Multicenter, Retrospective, Observational Study
Ye Seul Yang, Nam Hoon Kim, Jong Ha Baek, Seung-Hyun Ko, Jang Won Son, Seung-Hwan Lee, Sang Youl Rhee, Soo-Kyung Kim, Tae Seo Sohn, Ji Eun Jun, In-Kyung Jeong, Chong Hwa Kim, Keeho Song, Eun-Jung Rhee, Junghyun Noh, Kyu Yeon Hur
Diabetes & Metabolism Journal.2024; 48(2): 279. CrossRef - Renoprotective Mechanism of Sodium-Glucose Cotransporter 2 Inhibitors: Focusing on Renal Hemodynamics
Nam Hoon Kim, Nan Hee Kim
Diabetes & Metabolism Journal.2022; 46(4): 543. CrossRef - Real-World Prescription Patterns and Barriers Related to the Use of Sodium-Glucose Cotransporter 2 Inhibitors among Korean Patients with Type 2 Diabetes Mellitus and Cardiovascular Disease
Jong Ha Baek, Ye Seul Yang, Seung-Hyun Ko, Kyung Do Han, Jae Hyeon Kim, Min Kyong Moon, Jong Suk Park, Byung-Wan Lee, Tae Jung Oh, Suk Chon, Jong Han Choi, Kyu Yeon Hur
Diabetes & Metabolism Journal.2022; 46(5): 701. CrossRef
- Real-World Treatment Patterns according to Clinical Practice Guidelines in Patients with Type 2 Diabetes Mellitus and Established Cardiovascular Disease in Korea: Multicenter, Retrospective, Observational Study
- Metabolic Risk/Epidemiology
- Importance of Awareness and Treatment for Diabetes in Influenza Vaccination Coverage of Diabetic Patients under 65 Years: A Population-Based Study
- Yu Mi Ko, Seung Hyun Ko, Kyoungdo Han, Yong-Moon Park, Joon Young Choi, Shin Young Kim, So Hyang Song, Chi Hong Kim, Sung Kyoung Kim
- Diabetes Metab J. 2021;45(1):55-66. Published online May 29, 2020
- DOI: https://doi.org/10.4093/dmj.2019.0189
- 6,988 View
- 138 Download
- 6 Web of Science
- 5 Crossref
-
 Abstract
Abstract
 PDF
PDF PubReader
PubReader  ePub
ePub Background Influenza is a global public health problem causing considerable morbidity and mortality. Although vaccination is the most effective way to prevent infection, vaccination coverage is insufficient in people with chronic disease under 65 years, especially diabetes. The purpose of this study was to evaluate influenza vaccination coverage and identify factors associated with influenza vaccination in Korean diabetic adults under 65 years.
Methods Data were obtained from 24,821 subjects in the Korea National Health and Nutrition Examination Survey (2014 to 2017). Socioeconomic, health-related, and diabetic factors were investigated for their relations with influenza vaccination in diabetic patients under 65 years using univariate and multivariate analyses.
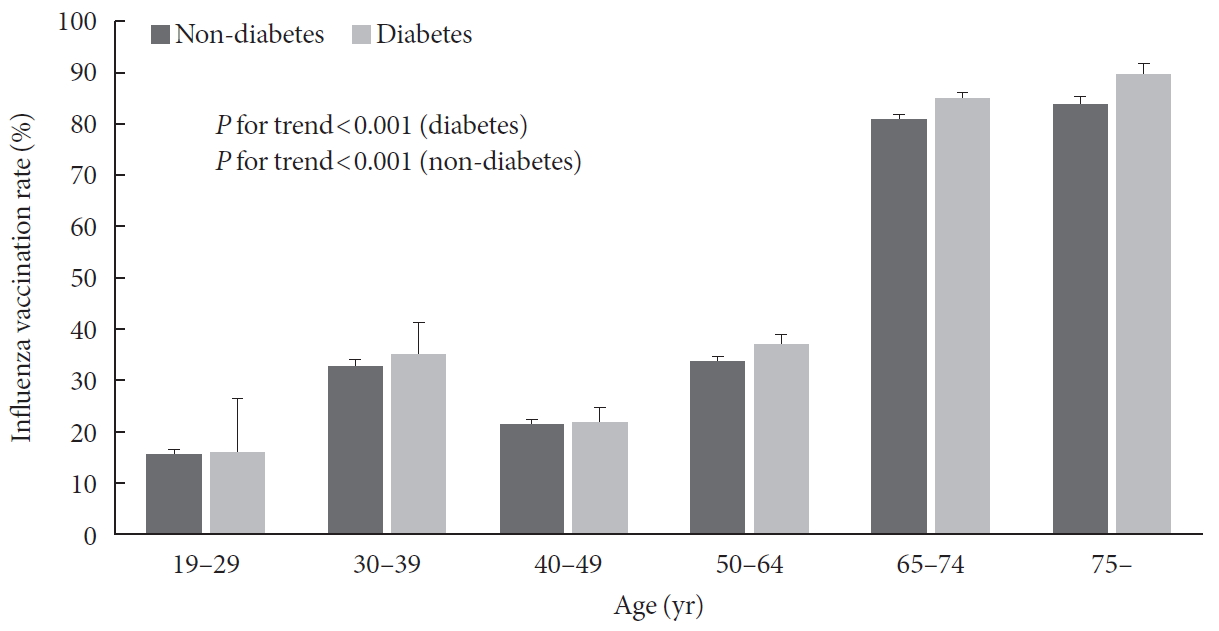
Results Among 24,821 subjects, 1,185 were diabetic patients under 65 years and their influenza vaccination rate was 36.5%. Socioeconomic (older age, female gender, non-smoker, light alcohol drinker, lower educational level, and employed status), health-related factors (lower fasting glucose and glycosylated hemoglobin level, good self-perceived health status, more comorbidities, recent health screening, more outpatient visits, and diet therapy), and diabetic factors (more awareness and getting treated) were associated with influenza vaccination. In multivariate analysis, more awareness and getting treated for diabetes were associated with influenza vaccination in diabetic patients under 65 years (odds ratio, 1.496 and 1.413; 95% confidence interval, 1.022 to 2.188 and 1.018 to 2.054, respectively).
Conclusion Influenza vaccination rate was low in diabetic patients under 65 years, especially in those with unawareness and not getting treated for diabetes. Active screening and treatment for diabetes may be helpful to improve the influenza vaccination rate in these patients.
-
Citations
Citations to this article as recorded by- Adherence to Advisory Committee on Immunization Practices in diabetes mellitus patients in Saudi Arabia: A multicenter retrospective study
Saleh Fahad Alqifari, Aya K Esmail, Dalal M Alarifi, Ghalya Y Alsuliman, Maram M Alhati, May R Mutlaq, Mohammed Aldhaeefi, Shaden A Alshuaibi, Palanisamy Amirthalingam, Abrar Abdallah, Afaf S Wasel, Heba R Hamad, Shoroq Alamin, Tasneem H Atia, Tariq Alqah
World Journal of Diabetes.2024; 15(3): 440. CrossRef - ЕГДЕ ЖАСТАҒЫ АДАМДАРДА COVID-19 ВАКЦИНАЦИЯСЫНЫҢ ТИІМДІЛІГІ
Ю.Р. АБДУСАТТАРОВА, Д.С. ӘБЕН, Н. АБДОЛЛА, Р.Т. ТЛЕУЛИЕВА, А. КАЛИ, Ю.В. ПЕРФИЛЬЕВА
Vestnik.2023; (2(65)): 59. CrossRef - Comorbidities associated with high-risk obstructive sleep apnea based on the STOP-BANG questionnaire: a nationwide population-based study
Gene Huh, Kyoung do Han, Yong-Moon Park, Chan-Soon Park, Kyu-na Lee, Eun Young Lee, Jung-Hae Cho
The Korean Journal of Internal Medicine.2023; 38(1): 80. CrossRef - Influenza vaccination trend and related factors among patients with diabetes in Korea: Analysis using a nationwide database
Dong-Hwa Lee, Bumhee Yang, Seonhye Gu, Eung-Gook Kim, Youlim Kim, Hyung Koo Kang, Yeong Hun Choe, Hyun Jeong Jeon, Seungyong Park, Hyun Lee
Frontiers in Endocrinology.2023;[Epub] CrossRef - Factors associated with seasonal influenza immunization in people with chronic diseases
Slađana Arsenović, Tatjana Gazibara
Medicinski podmladak.2021; 72(2): 19. CrossRef
- Adherence to Advisory Committee on Immunization Practices in diabetes mellitus patients in Saudi Arabia: A multicenter retrospective study
- Guideline/Fact Sheet
- Metformin Treatment for Patients with Diabetes and Chronic Kidney Disease: A Korean Diabetes Association and Korean Society of Nephrology Consensus Statement
- Kyu Yeon Hur, Mee Kyoung Kim, Seung Hyun Ko, Miyeun Han, Dong Won Lee, Hyuk-Sang Kwon
- Diabetes Metab J. 2020;44(1):3-10. Published online February 21, 2020
- DOI: https://doi.org/10.4093/dmj.2020.0004
- 9,478 View
- 333 Download
- 14 Web of Science
- 13 Crossref
-
 Abstract
Abstract
 PDF
PDF Supplementary Material
Supplementary Material PubReader
PubReader The safety of metformin use for patients with type 2 diabetes mellitus (T2DM) and advanced kidney disease is controversial, and more recent guidelines have suggested that metformin be used cautiously in this group until more definitive evidence concerning its safety is available. The Korean Diabetes Association and the Korean Society of Nephrology have agreed on consensus statements concerning metformin use for patients with T2DM and renal dysfunction, particularly when these patients undergo imaging studies using iodinated contrast media (ICM). Metformin can be used safely when the estimated glomerular filtration rate (eGFR) is ≥45 mL/min/1.73 m2. If the eGFR is between 30 and 44 mL/min/1.73 m2, metformin treatment should not be started. If metformin is already in use, a daily dose of ≤1,000 mg is recommended. Metformin is contraindicated when the eGFR is <30 mL/min/1.73 m2. Renal function should be evaluated prior to any ICM-related procedures. During procedures involving intravenous administration of ICM, metformin should be discontinued starting the day of the procedures and up to 48 hours post-procedures if the eGFR is <60 mL/min/1.73 m2.
-
Citations
Citations to this article as recorded by- Distribution and elimination kinetics of midazolam and metabolites after post-resuscitation care: a prospective observational study
Wonjoon Jeong, Jung Sunwoo, Yeonho You, Jung Soo Park, Jin Hong Min, Yong Nam In, Hong Joon Ahn, So Young Jeon, Jang Hee Hong, Ji Hye Song, Hyein Kang, My Tuyen Thi Nguyen, Jaehan Kim, Changshin Kang
Scientific Reports.2024;[Epub] CrossRef - Prediction of glycosylated hemoglobin level in patients with cardiovascular diseases and type 2 diabetes mellitus with respect to anti-diabetic medication
Alisher Ikramov, Shakhnoza Mukhtarova, Raisa Trigulova, Dilnoza Alimova, Saodat Abdullaeva
Frontiers in Endocrinology.2024;[Epub] CrossRef - Determinants of vitamin B12 deficiency in patients with type-2 diabetes mellitus — A primary-care retrospective cohort study
Andrew Kien Han Wee, Rehena Sultana
BMC Primary Care.2023;[Epub] CrossRef - Risk factors for post-contrast acute kidney injury in patients sequentially administered iodine- and gadolinium-based contrast media on the same visit to the emergency department: a retrospective study
Changshin Kang, Soo Hyun Han, Jung Soo Park, Dae Eun Choi
Kidney Research and Clinical Practice.2023; 42(3): 358. CrossRef - Guideline for the diagnosis and treatment of diabetes mellitus in patients with transfusion-dependent thalassemia
Mohammad E. Khamseh, Mojtaba Malek, Nahid Hashemi-madani, Fariba Ghassemi, Neda Rahimian, Amir Ziaee, Mohammad Reza Foroughi-Gilvaee, Pooya Faranoush, Negin Sadighnia, Ali Elahinia, Mohammad Reza Rezvany, Mohammad Faranoush
Iranian Journal of Blood and Cancer.2023; 15(4): 293. CrossRef - Continuous use of metformin in patients receiving contrast medium: what is the evidence? A systematic review and meta-analysis
Ting-Wan Kao, Kuo-Hua Lee, Wing P. Chan, Kang-Chih Fan, Che-Wei Liu, Yu-Chen Huang
European Radiology.2022; 32(5): 3045. CrossRef - Glucagon-Like Peptide-1 Receptor Agonists in Type 2 Diabetes Mellitus and Cardiovascular Disease: The Past, Present, and Future
Filipe Ferrari, Rafael S. Scheffel, Vítor M. Martins, Raul D. Santos, Ricardo Stein
American Journal of Cardiovascular Drugs.2022; 22(4): 363. CrossRef - Comparative Efficacy of Lobeglitazone Versus Pioglitazone on Albuminuria in Patients with Type 2 Diabetes Mellitus
Kyung-Soo Kim, Sangmo Hong, Hong-Yup Ahn, Cheol-Young Park
Diabetes Therapy.2021; 12(1): 171. CrossRef - Treatment Patterns of Type 2 Diabetes Assessed Using a Common Data Model Based on Electronic Health Records of 2000–2019
Kyung Ae Lee, Heung Yong Jin, Yu Ji Kim, Yong-Jin Im, Eun-Young Kim, Tae Sun Park
Journal of Korean Medical Science.2021;[Epub] CrossRef - Albuminuria Is Associated with Steatosis Burden in Patients with Type 2 Diabetes Mellitus and Nonalcoholic Fatty Liver Disease (Diabetes Metab J 2021;45:698-707)
Eugene Han, Hye Soon Kim
Diabetes & Metabolism Journal.2021; 45(6): 972. CrossRef - KRCP's past and future path
Tae-Hyun Yoo
Kidney Research and Clinical Practice.2020; 39(3): 233. CrossRef - Metformin Use and Risk of All-Cause Mortality and Cardiovascular Events in Patients With Chronic Kidney Disease—A Systematic Review and Meta-Analysis
Yao Hu, Min Lei, Guibao Ke, Xin Huang, Xuan Peng, Lihui Zhong, Ping Fu
Frontiers in Endocrinology.2020;[Epub] CrossRef - Pharmacotherapy for patients with diabetes mellitus
Joon Ho Moon, Soo Lim
Journal of the Korean Medical Association.2020; 63(12): 766. CrossRef
- Distribution and elimination kinetics of midazolam and metabolites after post-resuscitation care: a prospective observational study
- Transdifferentiation of Enteroendocrine K-cells into Insulin-expressing Cells.
- Esder Lee, Jun Mo Yu, Min Kyung Lee, Gyeong Ryul Ryu, Seung Hyun Ko, Yu Bae Ahn, Sung Dae Moon, Ki Ho Song
- Korean Diabetes J. 2009;33(6):475-484. Published online December 1, 2009
- DOI: https://doi.org/10.4093/kdj.2009.33.6.475
- 2,221 View
- 19 Download
- 1 Crossref
-
 Abstract
Abstract
 PDF
PDF - BACKGROUND
Despite a recent breakthough in human islet transplantation for treating type 1 diabetes mellitus, the limited availability of donor pancreases remains a major obstacle. Endocrine cells within the gut epithelium (enteroendocrine cells) and pancreatic beta cells share similar pathways of differentiation during embryonic development. In particular, K-cells that secrete glucose-dependent insulinotropic polypeptide (GIP) have been shown to express many of the key proteins found in beta cells. Therefore, we hypothesize that K-cells can be transdifferentiated into beta cells because both cells have remarkable similarities in their embryonic development and cellular phenotypes. METHODS: K-cells were purified from heterogeneous STC-1 cells originating from an endocrine tumor of a mouse intestine. In addition, a K-cell subclone expressing stable Nkx6.1, called "Kn4-cells," was successfully obtained. In vitro differentiation of K-cells or Kn4-cells into beta cells was completed after exendin-4 treatment and serum deprivation. The expressions of insulin mRNA and protein were examined by RT-PCR and immunocytochemistry. The interacellular insulin content was also measured. RESULTS: K-cells were found to express glucokinase and GIP as assessed by RT-PCR and Western blot analysis. RT-PCR showed that K-cells also expressed Pdx-1, NeuroD1/Beta2, and MafA, but not Nkx6.1. After exendin-4 treatment and serum deprivation, insulin mRNA and insulin or C-peptide were clearly detected in Kn4-cells. The intracellular insulin content was also increased significantly in these cells. CONCLUSION: K-cells are an attractive potential source of insulin-producing cells for treatment of type 1 diabetes mellitus. However, more experiments are necessary to optimize a strategy for converting K-cells into beta cells. -
Citations
Citations to this article as recorded by- Reprogramming of enteroendocrine K cells to pancreatic β-cells through the combined expression of Nkx6.1 and Neurogenin3, and reaggregation in suspension culture
Esder Lee, Gyeong Ryul Ryu, Sung-Dae Moon, Seung-Hyun Ko, Yu-Bae Ahn, Ki-Ho Song
Biochemical and Biophysical Research Communications.2014; 443(3): 1021. CrossRef
- Reprogramming of enteroendocrine K cells to pancreatic β-cells through the combined expression of Nkx6.1 and Neurogenin3, and reaggregation in suspension culture
- Incidence of Diabetic Foot and Associated Risk Factors in Type 2 Diabetic Patients: A Five-year Observational Study.
- Shin Ae Park, Seung Hyun Ko, Seung Hwan Lee, Jae Hyoung Cho, Sung Dae Moon, Sang A Jang, Hyun Shik Son, Ki Ho Song, Bong Yun Cha, Ho Young Son, Yu Bae Ahn
- Korean Diabetes J. 2009;33(4):315-323. Published online August 1, 2009
- DOI: https://doi.org/10.4093/kdj.2009.33.4.315
- 2,390 View
- 36 Download
- 13 Crossref
-
 Abstract
Abstract
 PDF
PDF - BACKGROUND
The frequency of lower extremity amputation due to diabetic foot has been increasing in type 2 diabetic patients. The aim of this study was to observe the incidence, clinical aspects and associated risk factors for diabetic foot. METHODS: We evaluated the incidence of diabetic foot through a five-year observation of type 2 diabetic patients who presented to St. vincent's Hospital between January and December 2003. To identify the risk factors for diabetic foot, we evaluated mean glycosylated hemoglobin A1c (HbA1c) every six months and assessed renal function based on the existence of proteinuria and estimated glomerular filtration rate (GFR) using the Modification of Diet in Renal Disease (MDRD) equation. Patients were also evaluated for retinopathy, peripheral neuropathy and autonomic neuropathy using Ewing's method. RESULTS: From an initial pool of 613 patients, the observational study of 508 patients (82.9%) was completed. The mean age, duration of diabetes and HbA1c were 50.3 +/- 10.6 yrs, 7.2 +/- 6.5 yrs and 8.8 +/- 2.1%, respectively. Diabetic foot occurred in 32 patients (6.3%). The incidence of diabetic foot increased when diabetic retinopathy (OR = 6.707, 2.314~19.439), peripheral neuropathy (OR = 2.949, 1.075~8.090), and autonomic neuropathy (OR = 3.967, 1.476~10.660) were present and when the MDRD GFR (OR = 5.089, 1.712~15.130) decreased. Mean HbA1c (OR = 12.013, 1.470~98.179) was found to be an independent risk factor for diabetic foot. CONCLUSION: The present study confirmed the importance of intensive glycemic control and the role of autonomic dysfunction in the development of diabetic foot. In addition, diabetic retinopathy and impaired renal function proved to be factors associated with the occurrence of diabetic foot. Therefore, intensive glycemic control, as well as periodic examination of renal function, are essential for the prevention of diabetic foot. -
Citations
Citations to this article as recorded by- Microbiological, Clinical and Radiological Aspects of Diabetic Foot Ulcers Infected with Methicillin-Resistant and -Sensitive Staphylococcus aureus
Maria Stańkowska, Katarzyna Garbacz, Anna Korzon-Burakowska, Marek Bronk, Monika Skotarczak, Anna Szymańska-Dubowik
Pathogens.2022; 11(6): 701. CrossRef - Potential of Nanoencapsulated Quercetin Topical Formulations in the Management of Diabetic Foot Ulcer
Shashank Chaturvedi, Shruti Agrawal, Anuj Garg, Vaibhav Rastogi
Revista Brasileira de Farmacognosia.2022; 33(3): 484. CrossRef - Development of a Diabetic Foot Ulceration Prediction Model and Nomogram
Eun Joo Lee, Ihn Sook Jeong, Seung Hun Woo, Hyuk Jae Jung, Eun Jin Han, Chang Wan Kang, Sookyung Hyun
Journal of Korean Academy of Nursing.2021; 51(3): 280. CrossRef - Regional Variation in the Incidence of Diabetes-Related Lower Limb Amputations and Its Relationship with the Regional Factors
Sung Hun Won, Jahyung Kim, Dong-Il Chun, Young Yi, Suyeon Park, Kwang-Young Jung, Gun-Hyun Park, Jaeho Cho
Journal of Korean Foot and Ankle Society.2019; 23(3): 121. CrossRef - The Changes of Trends in the Diagnosis and Treatment of Diabetic Foot Ulcer over a 10-Year Period: Single Center Study
Choong Hee Kim, Jun Sung Moon, Seung Min Chung, Eun Jung Kong, Chul Hyun Park, Woo Sung Yoon, Tae Gon Kim, Woong Kim, Ji Sung Yoon, Kyu Chang Won, Hyoung Woo Lee
Diabetes & Metabolism Journal.2018; 42(4): 308. CrossRef - The Relationship between Body Mass Index and Diabetic Foot Ulcer, Sensory, Blood Circulation of Foot on Type II Diabetes Mellitus Patients
Yi Kyu Park, Jun Young Lee, Sung Jung, Kang Hyeon Ryu
Journal of the Korean Orthopaedic Association.2018; 53(2): 136. CrossRef - Factors Contributing to Diabetic Foot Ulcer among Patients with Type 2 Diabetes Mellitus
Seo Jin Park, Taeyoung Yang, Jun Young Lee, Jinhee Kim
Korean Journal of Adult Nursing.2018; 30(1): 106. CrossRef - A Report on Diabetic Foot and Amputation from the Korean Health Insurance Review & Assessment Service Data
Jong-Kil Kim, Young-Ran Jung, Kyung-Tae Kim, Chung-Shik Shin, Kwang-Bok Lee
Journal of Korean Foot and Ankle Society.2017; 21(2): 66. CrossRef - Prevalence and Current Status of Treatment of Diabetic Foot in South Korea
Jae-Ik Bae, Je Hwan Won, Jun Su Kim, Man Deuk Kim, Chang Jin Yoon, Yun Ku Cho
Journal of the Korean Society of Radiology.2016; 74(3): 169. CrossRef - Diabetic Foot Disease—Incidence and Risk Factors: A Clinical Study
Rajesh Kapila, Rakesh Sharma, Ashwani K Sharma, Jagsir Mann
Journal of Foot and Ankle Surgery (Asia Pacific).2016; 3(1): 41. CrossRef - Diabetic Peripheral Neuropathy in Type 2 Diabetes Mellitus in Korea
Seung-Hyun Ko, Bong-Yun Cha
Diabetes & Metabolism Journal.2012; 36(1): 6. CrossRef - Diabetics' Preference in the Design Factors and Performance Requirements of Diabetic Socks
Ji-Eun Lee, Young-Ah Kwon
Journal of the Korean Society of Clothing and Textiles.2011; 35(5): 527. CrossRef - Epidemiology of Diabetic Foot Disease
Kyu Jeung Ahn
Journal of Korean Diabetes.2011; 12(2): 72. CrossRef
- Microbiological, Clinical and Radiological Aspects of Diabetic Foot Ulcers Infected with Methicillin-Resistant and -Sensitive Staphylococcus aureus
- Effects of Anti-Vascular Endothelial Growth Factor (VEGF) on Pancreatic Islets in Mouse Model of Type 2 Diabetes Mellitus.
- Ji Won Kim, Dong Sik Ham, Heon Seok Park, Yu Bai Ahn, Ki Ho Song, Kun Ho Yoon, Ki Dong Yoo, Myung Jun Kim, In Kyung Jeong, Seung Hyun Ko
- Korean Diabetes J. 2009;33(3):185-197. Published online June 1, 2009
- DOI: https://doi.org/10.4093/kdj.2009.33.3.185
- 2,292 View
- 25 Download
-
 Abstract
Abstract
 PDF
PDF - BACKGROUND
Vascular endothelial growth factor (VEGF) is associated with the development of diabetic complications. However, it is unknown whether systemic VEGF treatment has any effects on the pancreatic islets in an animal model of type 2 diabetes mellitus. METHODS: Anti-VEGF peptide (synthetic ATWLPPR, VEGF receptor type 2 antagonist) was injected into db/db mice for 12 weeks. We analyzed pancreatic islet morphology and quantified beta-cell mass. Endothelial cell proliferation and the severity of islet fibrosis were also measured. VEGF expression in isolated islets was determined using Western blot analysis. RESULTS: When anti-VEGF was administered, db/db mice exhibited more severe hyperglycemia and associated delayed weight gain than non-treated db/db mice. Pancreas weight and pancreatic beta-cell mass were also significantly decreased in the anti-VEGF-treated group. VEGF and VEGF receptor proteins (types 1 and 2) were expressed in the pancreatic islets, and their expression was significantly increased in the db/db group compared with the db/dm group. However, the elevated VEGF expression was significantly reduced by anti-VEGF treatment compared with the db/db group. The anti-VEGF-treated group had more prominent islet fibrosis and islet destruction than db/db mice. Intra-islet endothelial cell proliferation was also remarkably reduced by the anti-VEGF peptide. CONCLUSION: Inhibition of VEGF action by the VEGF receptor 2 antagonist not only suppressed the proliferation of intra-islet endothelial cells but also accelerated pancreatic islet destruction and aggravated hyperglycemia in a type 2 diabetes mouse model. Therefore, the potential effects of anti-VEGF treatment on pancreatic beta cell damage should be considered.
- A Nationwide Survey about the Current Status of Glycemic Control and Complications in Diabetic Patients in 2006: The Committee of the Korean Diabetes Association on the Epidemiology of Diabetes Mellitus.
- Soo Lim, Dae Jung Kim, In Kyung Jeong, Hyun Shik Son, Choon Hee Chung, Gwanpyo Koh, Dae Ho Lee, Kyu Chang Won, Jeong Hyun Park, Tae Sun Park, Jihyun Ahn, Jaetaek Kim, Keun Gyu Park, Seung Hyun Ko, Yu Bae Ahn, Inkyu Lee
- Korean Diabetes J. 2009;33(1):48-57. Published online February 1, 2009
- DOI: https://doi.org/10.4093/kdj.2009.33.1.48
- 2,779 View
- 55 Download
- 43 Crossref
-
 Abstract
Abstract
 PDF
PDF - BACKGROUND
The Committee of the Korean Diabetes Association on the Epidemiology of Diabetes Mellitus performed a nationwide survey about the current status of glycemic control and diabetic complications in 2006. METHODS: The current study included 5,652 diabetic patients recruited from the rosters of endocrinology clinics of 13 tertiary hospitals in Korea. Age, gender, height, weight, waist circumference and blood pressure were investigated by standard method. Fasting and postprandial 2 hour glucose, glycosylated hemoglobin (HbA1c), lipid profiles, fasting insulin and c-peptide levels were measured. Microvascular (microalbuminuria, retinopathy and neuropathy) and macrovascular (coronary artery disease [CAD], cerebrovascular disease [CVD] and peripheral artery disease [PAD]) complications were reviewed in their medical records. RESULTS: Mean age of total subjects was 58.7 (+/- 11.6) years and duration of diabetes was 8.8 (0~50) years. Mean fasting and postprandial 2 hour glucose levels were 145.9 +/- 55.0 and 208.0 +/- 84.4 mg/dL, respectively. Their mean HbA1c was 7.9 +/- 1.9%: the percentage of patients within target goal of glycemic control (< 7% of HbA1c) was 36.7%. In this study, 30.3%, 38.3% and 44.6% of patients was found to have microalbuminuria, retinopathy and nephropathy, respectively. Prevalence of CAD, CVD and PAD was 8.7%, 6.7% and 3.0%, respectively. Diabetic complications were closely related with age, duration of diabetes and glycemic control, and this relationship was stronger in microvascular complications than macrovascular ones. CONCLUSION: Only about one third of patients with diabetes was found to reach target glycemic control in tertiary hospitals of Korea. More tight control is needed to reduce deleterious complications of diabetes in Korea. -
Citations
Citations to this article as recorded by- Risk of Diabetic Complications in Type 2 Diabetes Patients with Dementia: A Population-Based Study Using National Health Insurance Claims Data
Eun Sik Jeong, Ah-Young Kim, Hye-Young Kang
Drug Targets and Therapeutics.2023; 2(1): 49. CrossRef - Prevalence of thyroid disorders in type 2 diabetic patients – A 1-year cross-sectional study
RikitaRamesh Mudhol, ShivakumarVeeranna Turamari, RekhaRamesh Mudhol, B Srinivas
BLDE University Journal of Health Sciences.2022; 7(1): 56. CrossRef - Associations of fasting glucose and glycated hemoglobin with vitamin D levels according to diabetes mellitus status in Korean adults
Yerin Hwang, Jiyoung Jang, Myung-Hee Shin
Epidemiology and Health.2022; 44: e2022025. CrossRef - Atherectomy in Peripheral Artery Disease: Current and Future
Yohan Kwon, Jinoo Kim, Je-Hwan Won, Seong Ho Kim, Jeong-Eun Kim, Sung-Joon Park
Journal of the Korean Society of Radiology.2021; 82(3): 551. CrossRef - Diabetic Retinopathy and Related Clinical Practice for People with Diabetes in Korea: A 10-Year Trend Analysis
Yoo-Ri Chung, Kyoung Hwa Ha, Kihwang Lee, Dae Jung Kim
Diabetes & Metabolism Journal.2020; 44(6): 928. CrossRef - Current status of treatment of type 2 diabetes mellitus in Ningbo, China
Tianmeng Yang, Rongjiong Zheng, Qingmei Chen, Yushan Mao
Journal of Clinical Laboratory Analysis.2019;[Epub] CrossRef - Recently Uncontrolled Glycemia in Diabetic Patients Is Associated with the Severity of Intracranial Atherosclerosis
Nari Choi, Jeong-Yoon Lee, Jun-Sang Sunwoo, Hakjae Roh, Moo-Young Ahn, Sung-Tae Park, Kyung Bok Lee
Journal of Stroke and Cerebrovascular Diseases.2017; 26(11): 2615. CrossRef - The effect of educational program based on the precede-proceed model on improving self-care behaviors in a semi-urban population with type 2 diabetes referred to health centers of Bavi, Iran
Neda Barasheh, Ghodratollah Shakerinejad, Sedigheh Nouhjah, Mohammad Hossein Haghighizadeh
Diabetes & Metabolic Syndrome: Clinical Research & Reviews.2017; 11: S759. CrossRef - Increased prevalence of albuminuria in individuals with higher range of impaired fasting glucose: the 2011 Korea National Health and Nutrition Examination Survey
Jong Chul Won, Jae Won Hong, Jung Min Kim, Tae Nyun Kim, Jung Hyun Noh, Kyung Soo Ko, Byoung Doo Rhee, Dong-Jun Kim
Journal of Diabetes and its Complications.2015; 29(1): 50. CrossRef - Assessment of glycemic control in patients with type 2 diabetes mellitus treated with metformin–sulfonylurea combination: Results of a multicenter, cross‐sectional, observational study in Korea
Sin Gon Kim, Jong Ryeal Hahm, Duk Kyu Kim, Sung Rae Cho, Dong Seop Choi
Journal of Diabetes Investigation.2015; 6(3): 317. CrossRef - Current Status of Management in Type 2 Diabetes Mellitus at General Hospitals in South Korea
Jin-Hee Jung, Jung-Hwa Lee, Jin-Won Noh, Jeong-Eun Park, Hee-Sook Kim, Joo-Wha Yoo, Bok-Rye Song, Jeong-rim Lee, Myeong-Hee Hong, Hyang-Mi Jang, Young Na, Hyun-Joo Lee, Jeong-Mi Lee, Yang-Gyo Kang, Sun-Young Kim, Kang-Hee Sim
Diabetes & Metabolism Journal.2015; 39(4): 307. CrossRef - Kidney injury molecule-1 (Kim-1): an early biomarker for nephropathy in type II diabetic patients
Nahla E. El-Ashmawy, Enas A. El-Zamarany, Naglaa F. Khedr, Abeer I. Abd El-Fattah, Shereen A. Eltoukhy
International Journal of Diabetes in Developing Countries.2015; 35(S3): 431. CrossRef - The Effect of the Experience of Diabetes Education on Knowledge, Self-Care Behavior and Glycosylated Hemoglobin in Type 2 Diabetic Patients
Seung Hei Moon, Young Whee Lee, Ok-Kyung Ham, Soo-Hyun Kim
The Journal of Korean Academic Society of Nursing Education.2014; 20(1): 81. CrossRef - Clinical Characteristics of Diabetic Patients Transferred to Korean Referral Hospitals
Min Young Oh, Sang Soo Kim, In Joo Kim, In Kyu Lee, Hong Sun Baek, Hyoung Woo Lee, Min Young Chung
Diabetes & Metabolism Journal.2014; 38(5): 388. CrossRef - Current Status of Prescription in Type 2 Diabetic Patients from General Hospitals in Busan
Ji Hye Suk, Chang Won Lee, Sung Pyo Son, Min Cheol Kim, Jun Hyeob Ahn, Kwang Jae Lee, Ja Young Park, Sun Hye Shin, Min Jeong Kwon, Sang Soo Kim, Bo Hyun Kim, Soon Hee Lee, Jeong Hyun Park, In Joo Kim
Diabetes & Metabolism Journal.2014; 38(3): 230. CrossRef - The Influence of Admission Hypoglycemia on Clinical Outcomes in Acute Myocardial Infarction Patients with Diabetes Mellitus
Eun Jung Kim, Myung Ho Jeong, In Seok Jeong, Sang Gi Oh, Sang Hyung Kim, Young keun Ahn, Ju Han Kim, Young Jo Kim, Shung Chull Chae, Taek Jong Hong, In Whan Seong, Jei Keon Chae, Chong Jin Kim, Myeong Chan Cho, Ki Bae Seung, Hyo Soo Kim
Korean Journal of Medicine.2014; 87(5): 565. CrossRef - Duration of diabetes and effectiveness of insulin in the management of insulin-naïve Korean patients uncontrolled on oral antidiabetic drugs: a sub-analysis of the MOdaliTy of Insulin treatment eValuation (MOTIV) registry results
Sang Soo Kim, In Joo Kim, Yong Ki Kim, Kun Ho Yoon, Ho Young Son, Sung Woo Park, Yeon Ah Sung, Hong Sun Baek, Kyoung Soo Ha
Acta Diabetologica.2014; 51(4): 655. CrossRef - Is the Indicator Magnifying Window for Insulin Pens Helpful for Elderly Diabetic Patients?
Ju Hee Lee, Eun Shil Hong, Jung Hun Ohn, Young Min Cho
Diabetes & Metabolism Journal.2013; 37(2): 149. CrossRef - Prevalence of and Factors Associated with Albuminuria in the Korean Adult Population: The 2011 Korea National Health and Nutrition Examination Survey
Jong Chul Won, Yun Jeong Lee, Jung Min Kim, Sang Youb Han, Jung Hyun Noh, Kyung Soo Ko, Byoung Doo Rhee, Dong-Jun Kim, Harald Mischak
PLoS ONE.2013; 8(12): e83273. CrossRef - The Epidemiology of Diabetic Nephropathy
Jin Hwa Kim
The Journal of Korean Diabetes.2013; 14(1): 11. CrossRef - The Relationship between Neuropathic Pain and Glycemic Control, Self Management in Type II Diabetes Mellitus Patients
Yeong-Mi Seo, Won-Hee Choi
Journal of the Korea Academia-Industrial cooperation Society.2013; 14(4): 1774. CrossRef - Efficacy and Safety of Biphasic Insulin Aspart 30/70 in Type 2 Diabetes Suboptimally Controlled on Oral Antidiabetic Therapy in Korea: A Multicenter, Open-Label, Single-Arm Study
Kee-Ho Song, Jung Min Kim, Jung-Hyun Noh, Yongsoo Park, Hyun-Shik Son, Kyong Wan Min, Kyung Soo Ko
Diabetes & Metabolism Journal.2013; 37(2): 117. CrossRef - Comorbidity Study on Type 2 Diabetes Mellitus Using Data Mining
Hye Soon Kim, A Mi Shin, Mi Kyung Kim, Yoon Nyun Kim
The Korean Journal of Internal Medicine.2012; 27(2): 197. CrossRef - Low ankle-brachial index is an independent predictor of poor functional outcome in acute cerebral infarction
Jinkwon Kim, Dong Hyun Lee, Myoung-Jin Cha, Tae-Jin Song, Ji Hye Park, Hye Sun Lee, Chung Mo Nam, Hyo Suk Nam, Young Dae Kim, Ji Hoe Heo
Atherosclerosis.2012; 224(1): 113. CrossRef - Glucose, Blood Pressure, and Lipid Control in Korean Adults with Diagnosed Diabetes
Sun-Joo Boo
Korean Journal of Adult Nursing.2012; 24(4): 406. CrossRef - Diabetic Peripheral Neuropathy in Type 2 Diabetes Mellitus in Korea
Seung-Hyun Ko, Bong-Yun Cha
Diabetes & Metabolism Journal.2012; 36(1): 6. CrossRef - The Association of Self-Reported Coronary Heart Disease with Diabetes Duration in Korea
Hye Mi Kang, Yun Jeong Lee, Dong-Jun Kim
Diabetes & Metabolism Journal.2012; 36(5): 350. CrossRef - Response: The Prevalence of Peripheral Arterial Disease in Korean Patients with Type 2 Diabetes Mellitus Attending a University Hospital (Diabetes Metab J 2011;35:543-50)
Ji Hee Yu, Ki-Up Lee
Diabetes & Metabolism Journal.2012; 36(1): 77. CrossRef - Reduction in glycated albumin can predict change in HbA1c: comparison of oral hypoglycaemic agent and insulin treatments
H. K. Won, K. J. Kim, B.‐W. Lee, E. S. Kang, B. S. Cha, H. C. Lee
Diabetic Medicine.2012; 29(1): 74. CrossRef - Management of Blood Pressure in Patients with Type 2 Diabetes Mellitus: A Nationwide Survey in Korean
Mi Hae Seo, Woo Je Lee, Cheol Young Park, Sung Rae Kim, Joong Yeol Park, Kun-Ho Yoon, Moon Kyu Lee, Sung Woo Park
Diabetes & Metabolism Journal.2011; 35(4): 348. CrossRef - Accuracy Evaluation of the Alternative Site Blood Glucose Test Using Error Grid
Kyung-Soon Park, Eun-Jong Cha
Journal of Biomedical Engineering Research.2011; 32(1): 25. CrossRef - Glycated albumin is a useful glycation index for monitoring fluctuating and poorly controlled type 2 diabetic patients
Eun Young Lee, Byung-Wan Lee, Daham Kim, Yong-ho Lee, Kwang Joon Kim, Eun Seok Kang, Bong-Soo Cha, Eun Jig Lee, Hyun Chul Lee
Acta Diabetologica.2011; 48(2): 167. CrossRef - Group Classification on Management Behavior of Diabetic Mellitus
Sung-Hong Kang, Soon-Ho Choi
Journal of the Korea Academia-Industrial cooperation Society.2011; 12(2): 765. CrossRef - Predictive Clinical Parameters for the Therapeutic Efficacy of Sitagliptin in Korean Type 2 Diabetes Mellitus
Soon Ae Kim, Woo Ho Shim, Eun Hae Lee, Young Mi Lee, Sun Hee Beom, Eun Sook Kim, Jeong Seon Yoo, Ji Sun Nam, Min Ho Cho, Jong Suk Park, Chul Woo Ahn, Kyung Rae Kim
Diabetes & Metabolism Journal.2011; 35(2): 159. CrossRef - Epidemiology of Micro- and Macrovascular Complications of Type 2 Diabetes in Korea
Jung Hee Kim, Dae Jung Kim, Hak Chul Jang, Sung Hee Choi
Diabetes & Metabolism Journal.2011; 35(6): 571. CrossRef - Increasing Trend in the Number of Severe Hypoglycemia Patients in Korea
Jin Taek Kim, Tae Jung Oh, Ye An Lee, Jun Ho Bae, Hyo Jeong Kim, Hye Seung Jung, Young Min Cho, Kyong Soo Park, Soo Lim, Hak Chul Jang, Hong Kyu Lee
Diabetes & Metabolism Journal.2011; 35(2): 166. CrossRef - Prevalence and Associated Factors of Diabetic Retinopathy in Rural Korea: The Chungju Metabolic Disease Cohort Study
Ji-Hyun Kim, Hyuk-Sang Kwon, Yong-Moon Park, Jin-Hee Lee, Man-Soo Kim, Kun-Ho Yoon, Won Chul Lee, Bong-Yun Cha, Ho-Young Son
Journal of Korean Medical Science.2011; 26(8): 1068. CrossRef - The Prevalence of Peripheral Arterial Disease in Korean Patients with Type 2 Diabetes Mellitus Attending a University Hospital
Ji Hee Yu, Jenie Yoonoo Hwang, Mi-Seon Shin, Chang Hee Jung, Eun Hee Kim, Sang Ah Lee, Eun Hee Koh, Woo Je Lee, Min-Seon Kim, Joong-Yeol Park, Ki-Up Lee
Diabetes & Metabolism Journal.2011; 35(5): 543. CrossRef - Prevalence, Awareness, and Control of Hypertension among Diabetic Koreans
Hyun Hee Chung, Kyu Chang Won
Diabetes & Metabolism Journal.2011; 35(4): 337. CrossRef - Factors Influencing Physical Activity Behavior among Iranian Women with Type 2 Diabetes Using the Extended Theory of Reasoned Action
Alireza Didarloo, Davoud Shojaeizadeh, Hassan Eftekhar Ardebili, Shamsaddin Niknami, Ebrahim Hajizadeh, Mohammad Alizadeh
Diabetes & Metabolism Journal.2011; 35(5): 513. CrossRef - Factors that Affect Medication Adherence in Elderly Patients with Diabetes Mellitus
Kyung-Ae Park, Jung-Guk Kim, Bo-Wan Kim, Sin Kam, Keon-Yeop Kim, Sung-Woo Ha, Sung-Taek Hyun
Korean Diabetes Journal.2010; 34(1): 55. CrossRef - The Effects of Tailored Diabetes Education on Blood Glucose Control and Self-Care
Kyung Sun Hyun, Kwang Mi Kim, Sook Hee Jang
Journal of Korean Academy of Nursing.2009; 39(5): 720. CrossRef - Epidemiologic Characteristics of Diabetes Mellitus in Korea: Current Status of Diabetic Patients Using Korean Health Insurance Database
Ie Byung Park, Sei Hyun Baik
Korean Diabetes Journal.2009; 33(5): 357. CrossRef
- Risk of Diabetic Complications in Type 2 Diabetes Patients with Dementia: A Population-Based Study Using National Health Insurance Claims Data
- Prevalence of the Metabolic Syndrome in Type 2 Diabetic Patients.
- Tae Ho Kim, Dae Jung Kim, Soo Lim, In Kyung Jeong, Hyun Shik Son, Choon Hee Chung, Gwanpyo Koh, Dae Ho Lee, Kyu Chang Won, Jeong Hyun Park, Tae Sun Park, Jihyun Ahn, Jaetaek Kim, Keun Gyu Park, Seung Hyun Ko, Yu Bae Ahn, Inkyu Lee
- Korean Diabetes J. 2009;33(1):40-47. Published online February 1, 2009
- DOI: https://doi.org/10.4093/kdj.2009.33.1.40
- 2,388 View
- 27 Download
- 13 Crossref
-
 Abstract
Abstract
 PDF
PDF - BACKGROUND
The aim of this study was to analyze the prevalence of metabolic syndrome in Korean type 2 diabetic patients. METHODS: A total of 4,240 diabetic patients (male 2,033, female 2,207; mean age 58.7 +/- 11.3 years; DM duration 8.9 +/- 7.6 years) were selected from the data of endocrine clinics of 13 university hospitals in 2006. Metabolic syndrome was defined using the criteria of the American Heart Association/National Heart Lung and Blood Institute and the criteria of waist circumference from the Korean Society for the Study of Obesity. RESULTS: The prevalence of metabolic syndrome was 77.9% (76.7% of males, 78.9% of females). The average number of the components of metabolic syndrome was 2.4 +/- 1.1. Abdominal obesity was seen in 56.8% of the patients, hypertriglyceridemia in 42.0%, low HDL cholesterol in 65.1%, and high blood pressure in 74.9%. Abdominal obesity and high blood pressure were much more prevalent among females than males, and low HDL cholesterol was much more prevalent among males than females. The prevalence of metabolic syndrome was not different according to the duration of diabetes. Metabolic syndrome was strongly related with obesity (odds ratio, 6.3) and increased age (odds ratio in the over 70 group, 3.4). CONCLUSION: The prevalence of metabolic syndrome was 77.9% in Korean type 2 diabetic patients. Its prevalence was greater in obese patients and in those over 40 years of age. -
Citations
Citations to this article as recorded by- A Novel Clinical Predictor of Metabolic Syndrome: Vascular Risk Age
Abdulrahman Naser, Didar Elif Akgün, Rengin Çetin Güvenç, Samet Sayılan, Özgen Şafak
Bagcilar Medical Bulletin.2023; 9(1): 1. CrossRef - Risk of Carotid Atherosclerosis in Subjects with Prediabetes Overlapping Metabolic Syndrome
Seol A Jang, Kyoung Min Kim, Seok Won Park, Chul Sik Kim
Metabolic Syndrome and Related Disorders.2022; 20(10): 599. CrossRef - Metabolic Age, an Index Based on Basal Metabolic Rate, Can Predict Individuals That are High Risk of Developing Metabolic Syndrome
Sarahi Vásquez-Alvarez, Sergio K. Bustamante-Villagomez, Gabriela Vazquez-Marroquin, Leonardo M. Porchia, Ricardo Pérez-Fuentes, Enrique Torres-Rasgado, Oscar Herrera-Fomperosa, Ivette Montes-Arana, M. Elba Gonzalez-Mejia
High Blood Pressure & Cardiovascular Prevention.2021; 28(3): 263. CrossRef - Metabolic syndrome among type 2 diabetic patients in Sub-Saharan African countries: A systematic review and meta-analysis
Wondimeneh Shibabaw Shiferaw, Tadesse Yirga Akalu, Mihretie Gedefaw, Denis Anthony, Ayelign Mengesha Kassie, Worku Misganaw Kebede, Henok Mulugeta, Getenet Dessie, Yared Asmare Aynalem
Diabetes & Metabolic Syndrome: Clinical Research & Reviews.2020; 14(5): 1403. CrossRef - Optimal Waist Circumference Cutoff Value Based on Insulin Resistance and Visceral Obesity in Koreans with Type 2 Diabetes
Jung Soo Lim, Young Ju Choi, Soo-Kyung Kim, Byoung Wook Huh, Eun Jig Lee, Kap Bum Huh
Diabetes & Metabolism Journal.2015; 39(3): 253. CrossRef - The Relations between Diabetic Dietary Compliance, Dietary Intake, and Physical Activity and the Prevalence of Metabolic Syndrome (MS) in Type 2 Diabetic Patients
Dong Eun Kim, Seung Hee Hong, Ji-Myung Kim
Korean Journal of Community Nutrition.2015; 20(5): 351. CrossRef - The Comparison between Periodontal Health Status and the Findings of Hypertension and Diabetes Disease of some Workers
In-Young Ku, Seon-Jeong Moon, Kyung-Hwan Ka, Myeong-Seon Lee
The Korean Journal of Health Service Management.2013; 7(2): 81. CrossRef - The Relationship between Factors of Metabolic Syndrome in Korean Adult Males and the Parents' Family History of Diabetes
Hyung-Su Park, Jin-Gyu Jeong, Jin-Ho Yu
The Journal of the Korea institute of electronic communication sciences.2013; 8(5): 779. CrossRef - Associations of serum fetuin-A levels with insulin resistance and vascular complications in patients with type 2 diabetes
Chan-Hee Jung, Bo-Yeon Kim, Chul-Hee Kim, Sung-Koo Kang, Sang-Hee Jung, Ji-Oh Mok
Diabetes and Vascular Disease Research.2013; 10(5): 459. CrossRef - Cardio-Metabolic Features of Type 2 Diabetes Subjects Discordant in the Diagnosis of Metabolic Syndrome
Sa Rah Lee, Ying Han, Ja Won Kim, Ja Young Park, Ji Min Kim, Sunghwan Suh, Mi-Kyoung Park, Hye-Jeong Lee, Duk Kyu Kim
Diabetes & Metabolism Journal.2012; 36(5): 357. CrossRef - Comorbidity Study on Type 2 Diabetes Mellitus Using Data Mining
Hye Soon Kim, A Mi Shin, Mi Kyung Kim, Yoon Nyun Kim
The Korean Journal of Internal Medicine.2012; 27(2): 197. CrossRef - Therapeutic Target Achievement in Type 2 Diabetic Patients after Hyperglycemia, Hypertension, Dyslipidemia Management
Ah Young Kang, Su Kyung Park, So Young Park, Hye Jeong Lee, Ying Han, Sa Ra Lee, Sung Hwan Suh, Duk Kyu Kim, Mi Kyoung Park
Diabetes & Metabolism Journal.2011; 35(3): 264. CrossRef - The Correlations between Extremity Circumferences with Total and Regional Amounts of Skeletal Muscle and Muscle Strength in Obese Women with Type 2 Diabetes
Hwi Ryun Kwon, Kyung Ah Han, Hee Jung Ahn, Jae Hyuk Lee, Gang Seo Park, Kyung Wan Min
Diabetes & Metabolism Journal.2011; 35(4): 374. CrossRef
- A Novel Clinical Predictor of Metabolic Syndrome: Vascular Risk Age
- Average Daily Risk Range-Index of Glycemic Variability-Related Factor in Type 2 Diabetic Inpatients.
- Shin Ae Park, Seung Hyun Ko, Seung Hwan Lee, Jae Hyung Cho, Sung Dae Moon, Sang A Jang, Ki Ho Song, Hyun Shik Son, Kun Ho Yoon, Bong Yun Cha, Ho Young Son, Yu Bae Ahn
- Korean Diabetes J. 2009;33(1):31-39. Published online February 1, 2009
- DOI: https://doi.org/10.4093/kdj.2009.33.1.31
- 2,346 View
- 25 Download
- 2 Crossref
-
 Abstract
Abstract
 PDF
PDF - BACKGROUND
It is known that chronic sustained hyperglycemia and its consequent oxidative stress causes diabetic complication in type 2 diabetes. It has been further proven that glycemic variability causes oxidative stress. The aim of this study is to measure the average daily risk range (ADDR)-index of glycemic variability, and to evaluate relevant variables. METHODS: We measured the blood glucose level of type 2 diabetic patients who were treated with multiple daily injections from January to July, 2008. The blood glucose levels were checked four times a day for 14 days and were conversed according to the ADRR formula. The degree of glycemic variability was categorized into non-fluctuation and fluctuation groups. We collected patient data on age, sex, duration of diabetes, body mass index, HOMA(IR), HOMA(betacell) and HbA1c. RESULTS: A total of 97 patients were enrolled in this study. The mean age, duration of diabetes, HbA1c and mean ADRR were 57.6 +/- 13.4, 11.5 +/- 8.5 years, 10.7 +/- 2.5%, and 26.6 +/- 9.8, respectively. We classified 18.5% of the patients to the non-fluctuation group, and 81.5% to the fluctuation group. ADRR was significantly correlated with duration of diabetes, fasting and postprandial glucose, fructosamine, HbA1c and BMI and HOMAbetacell. In addition, this study confirmed that BMI, HOMAbetacell and HbA1c were ADRR-related independent variables. CONCLUSION: ADRR can be used as an index for blood glucose fluctuation in type 2 diabetic patients. Measuring ADRR in patients with low BMI and a long duration of diabetes is helpful to improve the effectiveness of their care. -
Citations
Citations to this article as recorded by- Relationships between Thigh and Waist Circumference, Hemoglobin Glycation Index, and Carotid Plaque in Patients with Type 2 Diabetes
Myung Ki Yoon, Jun Goo Kang, Seong Jin Lee, Sung-Hee Ihm, Kap Bum Huh, Chul Sik Kim
Endocrinology and Metabolism.2020; 35(2): 319. CrossRef - Reversal of Hypoglycemia Unawareness with a Single-donor, Marginal Dose Allogeneic Islet Transplantation in Korea: A Case Report
Hae Kyung Yang, Dong-Sik Ham, Heon-Seok Park, Marie Rhee, Young Hye You, Min Jung Kim, Ji-Won Kim, Seung-Hwan Lee, Tae Ho Hong, Byung Gil Choi, Jae Hyoung Cho, Kun-Ho Yoon
Journal of Korean Medical Science.2015; 30(7): 991. CrossRef
- Relationships between Thigh and Waist Circumference, Hemoglobin Glycation Index, and Carotid Plaque in Patients with Type 2 Diabetes
- Effect of Valsartan on Blood Pressure and Urinary Albumin Excretion in Hypertensive Type 2 Diabetic Patients: An Open-Label, Multicenter Study.
- Se Jun Park, Dae Jung Kim, Hae Jin Kim, Soo Yeon Park, Ji A Seo, Nan Hee Kim, Sung Hee Choi, Soo Lim, Hak Chul Jang, Seung Hyun Ko, Ki Ho Song, Yu Bae Ahn, Soo Kyoung Kim, Yong Wook Cho, Jun Goo Kang, Sung Hee Ihm, Cheol Young Park, Sung Woo Park, Dong Hyun Shin, Yong Hyun Kim, Kwan Woo Lee
- Korean Diabetes J. 2008;32(6):513-521. Published online December 1, 2008
- DOI: https://doi.org/10.4093/kdj.2008.32.6.513
- 2,298 View
- 25 Download
-
 Abstract
Abstract
 PDF
PDF - BACKGROUND
Activation of renin-angiotensin system (RAS) has been an important mechanism of microvascular and macrovascular complications in diabetic patients. It has been reported that RAS blockades reduce the development and progression of diabetic nephropathy. The aim of this study was to evaluate whether valsartan, an angiotensin II receptor blocker (ARB), reduced blood pressure and urinary albumin excretion rate (UAER) in hypertensive type 2 diabetic patients. METHOD: Three hundred forty-seven hypertensive type 2 diabetic patients who had not taken angiotensin converting enzyme inhibitors or ARB for 6 months prior to this study were enrolled. We measured blood pressure and UAER before and after 24 weeks of valsartan treatment. RESULT: Baseline mean systolic and diastolic blood pressure was 143 +/- 15 and 87 +/- 11 mmHg, respectively and the median albumin excretion rate was 27 ug/mg. Reduction in systolic and diastolic blood pressure was 16 mmHg/10 mmHg and the median UAER was 19.3 ug/mg after 24 weeks (P < 0.01, respectively). When we divided the subjects into three groups according to the UAER (normoalbuminuria, microalbuminuria and macroalbuminuria), significant changes were reported in the microalbuminuria and the macroalbuminuria groups. Thirty-eight (42%) patients with microalbuminuria improved to normoalbuminuria and twelve (41%) patients with macroalbuminuria improved to microalbuminuria. We found an association between the improvement of blood pressure and UAER (R = 0.165, P = 0.015). CONCLUSION: We concluded that valsartan reduces urinary albumin excretion and blood pressure in hypertensive type 2 diabetic patients.
- AICAR Reversed the Glucolipotoxicity Induced beta-cell Dysfunction through Suppression of PPAR-gamma-coactivator-1 (PGC-1) Overexpression.
- Hyuk Sang Kwon, Ji Won Kim, Heon Seok Park, Seung Hyun Ko, Bong Yun Cha, Ho Young Son, Kun Ho Yoon
- Korean Diabetes J. 2007;31(4):310-318. Published online July 1, 2007
- DOI: https://doi.org/10.4093/jkda.2007.31.4.310
- 2,022 View
- 21 Download
-
 Abstract
Abstract
 PDF
PDF - BACKGROUND
Glucolipotoxicity plays an important role in the progression of type 2 diabetes mellitus via inducing insulin secretory dysfunction. Expression of insulin gene in pancreatic beta cell might be regulated by AMP-activated protein kinase (AMPK), which is recognized as a key molecule of energy metabolism. We studied the effects of AMPK on glucolipotoxicity-induced beta-cell dysfunction by suppression of PPAR-gamma-coactivator-1 (PGC-1) in vitro and in vivo. Method: Glucolipotoxicity was induced by 33.3 mM glucose and 0.6 mM (palmitate and oleate) for 3 days in isolated rat islets. Messenger RNA (mRNA) expressions of beta-cell specific gene like insulin, BETA2/NeuroD and PGC-1 induced by glucolipotoxic condition and their changes with 5-aminoimidazole-4-carboxy-amide-1-D-ribofuranoside (AICAR) treatment were investigated using RT-PCR. We also examined glucose stimulated insulin secretion in same conditions. Furthermore, SD rats were submitted to a 90% partial pancreatectomy (Px) and randomized into two groups; Ad-GFP-infected Px rats (n = 3) and Ad-siPGC- 1-infected Px rats (n = 3). Then, the Px rats were infected with Ad-GFP or Ad-siPGC-1 (1 x 10(9) pfu) via celiac artery. After 12 days of viral infection, we measured body weight and performed the intraperitoneal glucose tolerance test (IP-GTT). RESULTS: Glucolipotoxicity resulted in blunting of glucose-stimulated insulin secretion, which was recovered by the AICAR treatment in vitro. Suppression in their expressions of insulin and BETA2/NeuroD gene by glucolipotoxic condition were improved with AICAR treatment. However, PGC-1alpha expression was gradually increased by glucolipotoxicity, and suppressed by AICAR treatment. Overexpression of PGC-1 using an adenoviral vector in freshly isolated rat islets suppressed insulin gene expression. We also confirmed the function of PGC-1 using an Ad-siPGC-1 in vivo. Direct infection of Ad-siPGC-1 in 90% pancreatectomized rats significantly improved glucose tolerance and increased body weight. CONCLUSION: AMPK could protect against glucolipotoxicity induced beta-cell dysfunction and the suppression of PGC-1 gene expression might involved in the insulin regulatory mechanism by AMPK.
- Differentiation of Pancreatic beta Cells from Human Pancreatic Duct Cells Derived from a Partial Pancreas Tissue.
- Ki Ho Song, Myung Mee Kim, Min Kyung Lee, Gyeong Ryul Ryu, Seung Hyun Ko, Sung Dae Moon, Yu Bae Ahn, Kun Ho Yoon, Bong Yun Cha, Kwang Woo Lee, Ho Young Son, Sung Koo Kang, Hyung Min Chin
- Korean Diabetes J. 2007;31(3):236-242. Published online May 1, 2007
- DOI: https://doi.org/10.4093/jkda.2007.31.3.236
- 1,956 View
- 23 Download
- 1 Crossref
-
 Abstract
Abstract
 PDF
PDF - BACKGROUND
Despite a recent breakthrough in human islet transplantation for treating diabetes mellitus, the limited availability of insulin-producing tissue is still a major obstacle. This has led to a search for alternative sources of transplantable insulin-producing cells including pancreatic duct cells. We aimed to establish in vitro culture of pancreatic duct cells from a partial pancreas tissue in human, which could be harnessed to differentiate into pancreatic beta cells. METHODS: We isolated pancreatic duct cells from small pieces of pancreas tissue (1~3 g) derived from non-diabetic humans (n = 8) undergoing pancreatic surgery due to cancer. Pancreas tissue was finely minced after injection of collagenase P into the parenchyma. The mince was incubated in a shaking water bath at 37degrees C for 25 min and passed through a 150 micrometer mesh. The released cells were recovered, washed, and plated in a dish containing CMRL culture medium with serum. RESULTS: Isolated pancreatic cells grew in monolayer and became confluent in 1~2 wks showing typical epithelial cobblestone morphology. Immunochemistry demonstrated that ~90% of the cultured cells were cytokeratin7-positive duct cells. To induce beta cell differentiation, the cells were incubated in DMEM/F12 culture medium without serum. In addition, treatment with Matrigel overlay, exendin-4, cholera toxin or forskolin was done. Though beta cell differentiation was found by immunostaining and RT-PCR, the differentiation efficiency was very low. Over-expression of neurogenin-3 by recombinant adenovirus did not increase beta cell differentiation of the cultured duct cells significantly. CONCLUSION: We established in vitro culture of pancreatic duct cells from a partial pancreas tissue in human, which differentiate into pancreatic cells. However, a strategy to optimize beta cell differentiation in this model is needed. -
Citations
Citations to this article as recorded by- Transdifferentiation of Enteroendocrine K-cells into Insulin-expressing Cells
Esder Lee, Jun Mo Yu, Min Kyung Lee, Gyeong Ryul Ryu, Seung-Hyun Ko, Yu-Bae Ahn, Sung-Dae Moon, Ki-Ho Song
Korean Diabetes Journal.2009; 33(6): 475. CrossRef
- Transdifferentiation of Enteroendocrine K-cells into Insulin-expressing Cells
- Glucose-dependent Insulin Secretion from Genetically Engineered K-cells Using EBV-based Episomal Vector.
- Ju Hee Kim, Sung Dae Moon, Seung Hyun Ko, Yu Bai Ahn, Ki Ho Song, Hyang Sook Lim, Sook Kyung Lee, Soon Jip Yoo, Hyun Shik Son, Kun Ho Yoon, Bong Yun Cha, Ho Young Son, Sung Joo Kim, Je Ho Han
- Korean Diabetes J. 2007;31(1):9-21. Published online January 1, 2007
- DOI: https://doi.org/10.4093/jkda.2007.31.1.9
- 2,400 View
- 17 Download
- 2 Crossref
-
 Abstract
Abstract
 PDF
PDF - BACKGROUND
Type 1 diabetes mellitus is an autoimmune disease resulting in destruction of the pancreatic beta cells. Insulin gene therapy for these patients has been vigorously researched. The strategy for achieving glucose-dependent insulin secretion in gene therapy relies on glucose-responsive transcription of insulin mRNA and the constitutive secretory pathway of target non-beta cells. We observed that genetically engineered K-cells using Epstein-Barr virus (EBV)-based episomal vector can produce glucose-regulated insulin production. METHODS: Green fluorescent protein (GFP) or rat-preproinsulin (PPI) expression cassette transcriptionally controlled by the promoter of glucose dependent insulinotropic peptide (GIPP) is fused to pCEP4 containing the origin of replication (oriP) and Epstein-Barr virus nuclear antigen 1 (EBNA-1). CMV promoter was replaced by subcloning the GIPP into pCEP4 to generate pGIPP/CEP4. Two recombinant EBV-based episomal vectors, pGIPP/GFP/CEP4 and pGIPP/PPI/CEP4, were constructed. pGIPP/GFP/CEP4 and pGIPP/PPI/CEP4 containing K-cell specific GIPP were co-transfected into STC-1. K-cell was isolated from the clonal expansion of the fluorescent cells selected by hygromycin treatment in STC-1, and were analyzed for the expression of glucokinase (GK) or transcription factors involved in pancreas development. K-cells concurrently transfected with pGIPP/PPI/CEP4 and pGIPP/GFP/CEP4 were analyzed for the transcripts of PPI by RT-PCR, and for the glucose dependent insulin expression by immunocytochemistry or insulin assay using ultra-sensitive rat-specific insulin ELISA kit. RESULT: STC-1 was stably-transfected with pGIPP/GFP/CEP4 along with pGIPP/PPI/CEP4. Genetically selected fluorescent K-cells expressed GK and transcription factors involved in pancreas development. And K-cells transfected with pGIPP/PPI/CEP4 contained detectable levels of PPI transcripts and showed glucose-dependent immunoreactive insulin secretion. CONCLUSION: We identified genetically engineered K-cells which exert a glucose-dependent insulin expression using EBV-based episomal vector. The similarities between K-cells and pancreatic beta cells support that K-cells may make effective and ideal targeting cells for insulin gene therapy or alternative cell therapy. -
Citations
Citations to this article as recorded by- Relationship of traditional and nontraditional cardiovascular risk factors to coronary artery calcium in type 2 diabetes
Ju-Yeon Sim, Ju-Hee Kim, Yu-Bae Ahn, Ki-Ho Song, Je-Ho Han, Bong-Yun Cha, Sook-Kyung Lee, Sung-Dae Moon
Korean Diabetes Journal.2009; 33(6): 466. CrossRef - Transdifferentiation of Enteroendocrine K-cells into Insulin-expressing Cells
Esder Lee, Jun Mo Yu, Min Kyung Lee, Gyeong Ryul Ryu, Seung-Hyun Ko, Yu-Bae Ahn, Sung-Dae Moon, Ki-Ho Song
Korean Diabetes Journal.2009; 33(6): 475. CrossRef
- Relationship of traditional and nontraditional cardiovascular risk factors to coronary artery calcium in type 2 diabetes
- Inducible Nitric Oxide Synthase (iNOS) Expression in the Hypoxic Injury to Pancreatic Beta (MIN6) Cells.
- Seung Hyun Ko, Seung Bum Kim, Kyung Ryul Ryu, Ji Won Kim, Yu Bai Ahn, Sung Dae Moon, Sung Rae Kim, Jung Min Lee, Hyuk Snag Kwon, Kun Ho Yoon, Ki Ho Song
- Korean Diabetes J. 2006;30(5):336-346. Published online September 1, 2006
- DOI: https://doi.org/10.4093/jkda.2006.30.5.336
- 2,182 View
- 20 Download
-
 Abstract
Abstract
 PDF
PDF - BACKGROUND
Islet transplantation is an alternative potential strategy to cure type 1 diabetes mellitus. However, two or more donors are usually needed for one recipient because a substantial part of the graft becomes nonfunctional due to several factors including hypoxia. Though hypoxic exposure of pancreatic beta cells has been reported to induce apoptotic cell death, the molecular processes involved in hypoxia-induced cell death are poorly understood. In type I diabetes, Nitric Oxide (NO) is known as an important cytokine, involved in the pathogenesis of beta cell dysfunction. Pancreatic beta cells are sensitive to the induction of inducible nitric oxide synthase (iNOS) when stimulated by TNF-a or IL-1beta. But contribution of iNOS in response to hypoxia is not yet fully understood. METHODS: Mouse insulinoma cells (MIN6) were incubated in an anaerobic chamber (75% N2/15% CO2/5% H2) for up to 12 hours. Cell viability was measured after AO/PI staining. Caspase-3 activation was also determined using Western blot analysis. Nitric Oxide (NO) release into culture medium was measured using a Griess reagent. The expression of iNOS and PDX-1 mRNA and iNOS protein was examined using real time PCR and Western blot analysis. RESULTS: Marked cell death was observed within 6 hours after hypoxic exposure of MIN6 cells (control, < 5%; 2 hr, 11.0+/-7.6%; 6 hr, 46.2+/-12.8%, P < 0.05). Immunoreactivity to activated caspase-3 was observed at 2, 4 and 6 hrs. NO production was increased in a time dependent manner. Expression of iNOS mRNA and protein was significantly increased at 4 and 6 hour after hypoxia. iNOS expression was confirmed by immunostaining. Of note, Pdx-1 mRNA expression was markedly attenuated by hypoxic treatment. Pretreatment with a selective iNOS inhibitor, 1400 W, significantly prevented beta cell death induced by hypoxic injury. CONCLUSION: Our data suggest that iNOS-NO play an important role in hypoxic injury to MIN6 cells. Therefore, iNOS-NO might be a potential therapeutic target for improving engraftment of the transplanted islets and suppression of iNOS would be helpful for prevention of beta cells damage to hypoxic injury.

 KDA
KDA
 First
First Prev
Prev





